MACULAR DEGENERATION ASSOCIATED WITH AGE
DIABETIC RETINOPATHY
What do they consist of and what symptoms do they produce?
People with diabetes may have an eye disease called diabetic retinopathy. This disease occurs because high blood sugar levels eventually cause damage to the blood vessels of the retina. These damaged blood vessels do not work well, dilate (forming microaneurysms) and allow fluid to escape into the retina or below (diabetic macular edema) and cause bleeding and deposits (exudates). They can also close and prevent blood flow (retinal ischemia). Ischemia or lack of irrigation in the retina causes the secretion of angiogenic factors, that is, they generate new blood vessels but these are abnormal (we call them neovases), bleed easily causing vitreous hemorrhages and cause scarring and can even detach the retina. All these changes left to its evolution can make you lose vision.

Do I have to have surgery of my macular problem?
The changes in the retina occur progressively, at the beginning they are slight and gradually they can move forward.
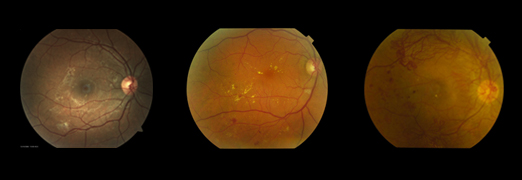
At the beginning of this process, if the central part of the retina is not affected, they may not cause visual problems, but it is important to detect those initial changes in order to act in time.
If the central part of the retina is affected (macular edema) you will notice alterations in the central vision: blurred vision and difficulty reading. In advanced cases, if vitreous hemorrhage or retinal detachment occurs, vision loss can be very severe and abrupt. The detection in the initial stages of this problem is very important because we have various treatments to be applied before irreversible damage to the retina is caused.
Therefore, all diabetics should be checked once a year even if they have no apparent visual problems. In case you already have any sign of retinopathy, depending on the severity of it, you should start some treatment or make more frequent reviews.
What does the surgery consist of?
Once the problem appears, your treatment will be different depending on the severity. These are some of the treatment options:
- Medical control of diabetes
Controlling your blood sugar can help stop vision loss. Follow the diet recommended by your nutritionist. Take the medications prescribed by your doctor. In some cases, good sugar control can even return some vision. Controlling blood pressure, cholesterol and getting some exercise can be of great help.
- Medication
The anti-VEGF or antiangiogenic (Eylea and Lucentis) help to improve the damage of the vessel walls and reduce macular edema. These drugs should be administered by the ophthalmologist according to different guidelines, by intravitreal injection.
Another option to reduce macular edema is treatment with corticosteroids. They are usually given in the form of injections or implants that last longer.
Your ophthalmologist will recommend the treatment plan appropriate to the severity of your retinopathy.
- Laser surgery
Laser surgery is used in diabetics to help seal blood vessels that suffer loss of fluid, improve oxygenation of the retina, make abnormal vessels disappear and stop vision loss. In most cases, it is necessary to perform more than one treatment and combine it with the previous ones.
- Vitrectomy
In advanced cases, if you have persistent vitreous hemorrhage, retinal traction or retinal detachment, it may be insufficient with previous treatments and you may need treatment with retinal surgery or vitrectomy. This operation involves removing the vitreous gel, cleaning the blood and improving the oxygenation of the retina, removing the scar tissue, repairing the detachment if there is one and sometimes completing the laser treatment.


You must be logged in to post a comment.